用两个队列实现一个栈
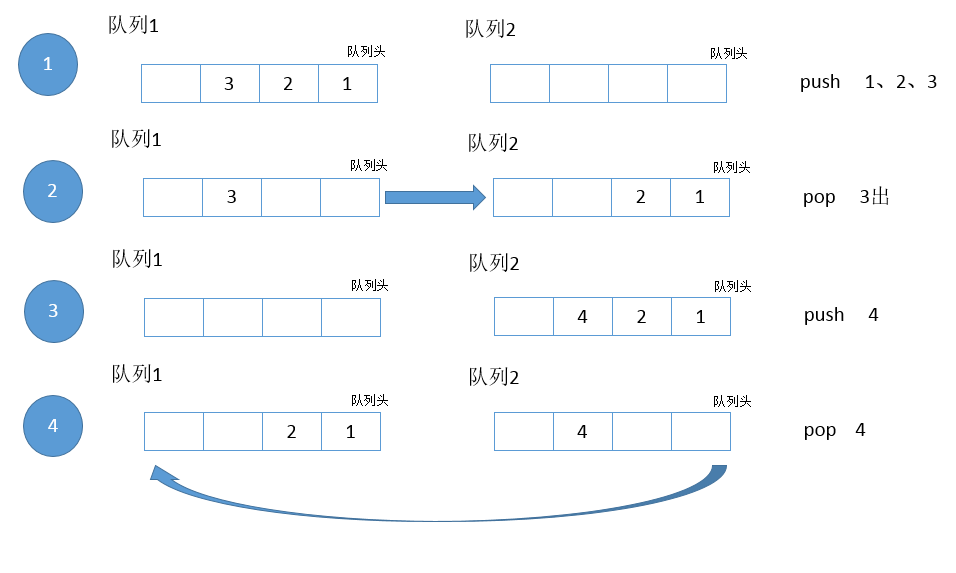
基本思想如上图所示:
在push的时候,往非空的那个队列添加(刚刚初始化的时候,两个队列都为空,随便往哪个队列push都行 上图步骤1和步骤3
在pop的时候,如果队列1不为空,就把队列1中q1.size()-1个元素poll出来,添加到队列2中(上图步骤2中元素1和2),再把队列中那个最后的元素poll出来(步骤2中元素3)
这两个队列中始终有一个是空的。另一个非空。push添加元素到非空队列中,pop把非空队列中前面的元素都转移到另一个队列中,只剩最后一个元素,再把最后一个元素pop出来。这样这一个队列是空的,另一个队列又非空了。
Java实现的代码:
class Stack{
LinkedList<Integer> queue1 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); //队列1
LinkedList<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); //队列2
// Push element x onto stack.
public void push(int x) {
if(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
}else{
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
// Removes the element on top of the stack.
public void pop() {
if(!empty()){
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
while(queue2.size() > 1){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
queue2.poll();
}else{
while(queue1.size() > 1){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
queue1.poll();
}
}
}
// Get the top element.
public int top() {
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
while(queue2.size() > 1){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
int x = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(x);
return x;
}else{
while(queue1.size() > 1){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
int x = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(x);
return x;
}
}
// Return whether the stack is empty.
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}
最新评论